What is a baclofen pump?
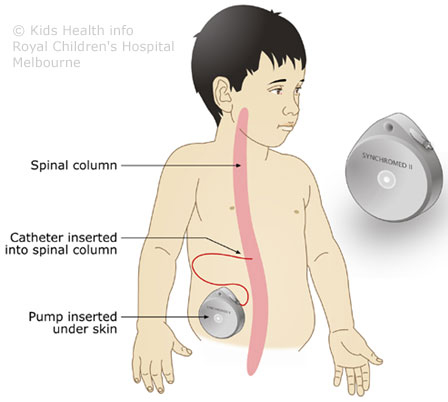
- Baclofen is one of the most effective drugs for dystonia (involuntary muscle spasms) and spasticity (stiff or rigid muscles) in NBIA
- A baclofen pump is surgically placed inside the body and continuously delivers baclofen
- When and how much baclofen gets delivered is programed into the pump by a doctor
- Baclofen is injected into the intrathecal space (fluid-filled area surrounding the spinal cord) through a catheter
When should a baclofen pump be considered?
- When oral baclofen medication can no longer control the dystonia/spasticity symptoms
- The oral form typically loses its effectiveness over time
- Side effects often develop before the oral drug reaches its full potential
- A baclofen pump should be considered as a alternate treatment earlier rather than later
What can be expected from the procedure?
- Before having baclofren pump surgery, individuals should first get a few test doses of baclofen
- They can be injected by a trained nurse in the hospital and kept overnight for observation
- The test doses will allow the doctor to see how a patient responds to the medication
- The baclofen pump can be placed either high or low depending on the surgeon
- Dr. A Leland Albright, a neurosurgeon at the University of Wisconsin, has developed a method to place the pump’s catheter tip high in the ventricle (fluid filled cavity) of the brain
- After the pump is implanted, regular doctor visits should be scheduled
- To re-evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment
- To adjust the level of medication as needed and how it is released from the pump to optimize results
- Other therapies such as oral medication, Botox injections and DBS (Deep Brain Stimulation) can be used along with a baclofen pump when appropriate/needed
What effect will it have on quality of life?
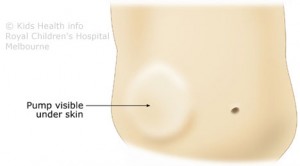
- The pump can sometimes be seen under clothing
- The pump needs to be refilled when the baclofen medication runs low
- However, it is generally discrete and has little effect on daily activities
Are there any side effects or cons?
Cons
- The surgical incision site can get infected
- Baclofen withdrawal or overdose
- Withdrawal is more likely than an overdose
- Something as simple as a kink in the tubing can lead to a lack of medication, causing withdrawal symptoms
- Human error can occur rarely, such as the medication dosage being programmed incorrectly into the pump and causing an overdose (vigilant parents can help reduce this risk)
Pros
- The baclofen pump is usually more effective than oral baclofen
- The baclofen pump is effective at a lower dose
- Lower dosage means fewer side effects and less harm to the body
- The baclofen pump can deliver medication in multiple ways:
- Continuous mode
- Flexible mode
- Or a combination of both based on trial and error
- The pump is less invasive than treatments like deep brain stimulation (DBS)
- DBS is probably the next best option for managing dystonia
- Treatment is potentially reversible because the pump can be removed if needed
Copyright © 2014 by NBIAcure.org. All rights reserved.